Swagger / Open API SupportTable of Contents
Table of Contents
API Platform natively support the Open API (formerly Swagger) API documentation format. It also integrates a customized version of Swagger UI, a nice tool to display the API documentation in a user friendly way.
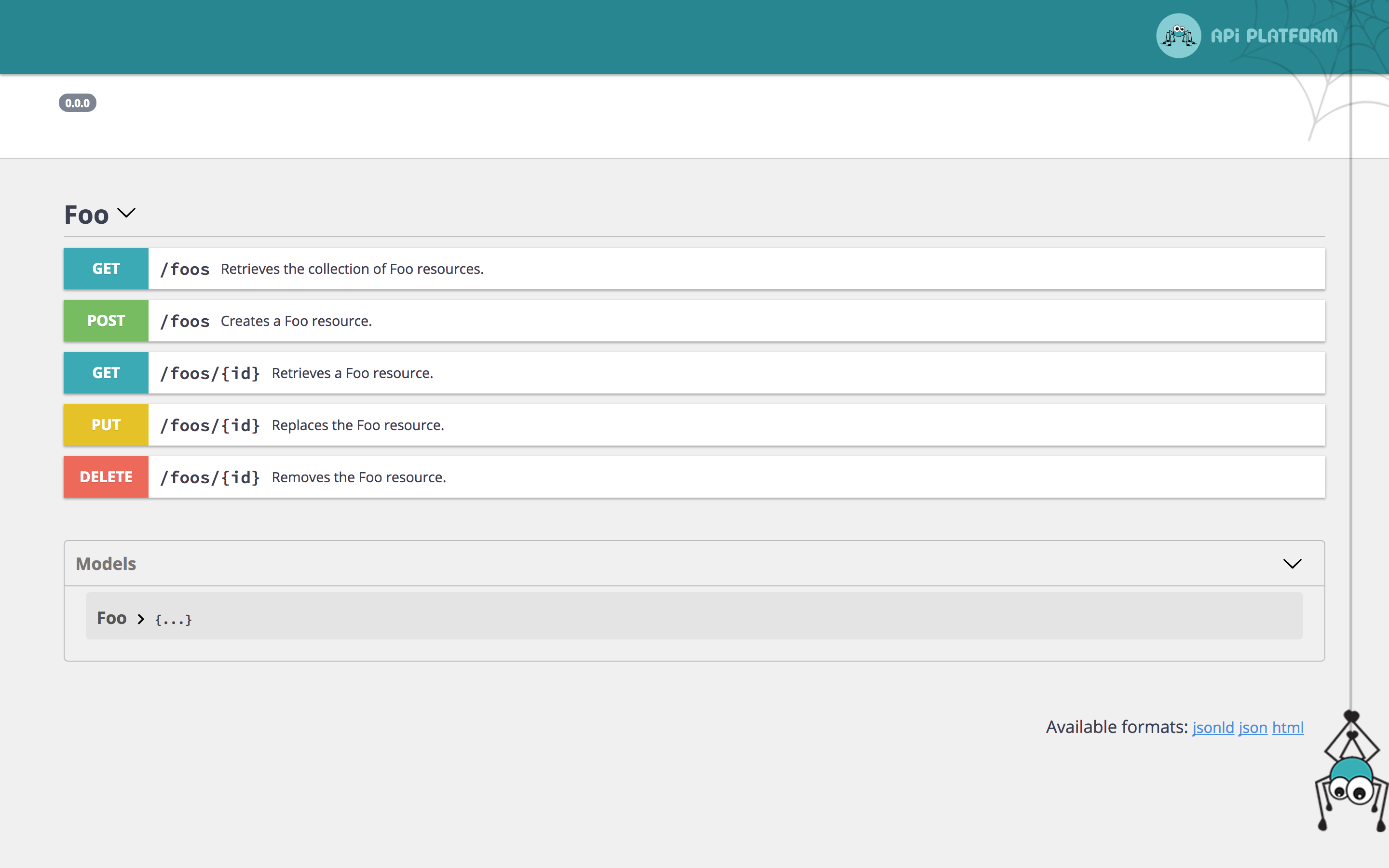
# Overriding the Swagger Documentation
Symfony allows to decorate services, here we
need to decorate api_platform.swagger.normalizer.documentation.
In the following example, we will see how to override the title of the Swagger documentation and add a custom filter for
the GET operation of /foos path
# api/config/services.yaml
services:
'App\Swagger\SwaggerDecorator':
decorates: 'api_platform.swagger.normalizer.documentation'
arguments: [ '@App\Swagger\SwaggerDecorator.inner' ]
autoconfigure: false<?php
// api/src/Swagger/SwaggerDecorator.php
namespace App\Swagger;
use Symfony\Component\Serializer\Normalizer\NormalizerInterface;
final class SwaggerDecorator implements NormalizerInterface
{
private $decorated;
public function __construct(NormalizerInterface $decorated)
{
$this->decorated = $decorated;
}
public function normalize($object, $format = null, array $context = [])
{
$docs = $this->decorated->normalize($object, $format, $context);
$customDefinition = [
'name' => 'fields',
'definition' => 'Fields to remove of the output',
'default' => 'id',
'in' => 'query',
];
// e.g. add a custom parameter
$docs['paths']['/foos']['get']['parameters'][] = $customDefinition;
// Override title
$docs['info']['title'] = 'My Api Foo';
return $docs;
}
public function supportsNormalization($data, $format = null)
{
return $this->decorated->supportsNormalization($data, $format);
}
}# Using the Swagger Context
Sometimes you may want to change the information included in your Swagger documentation. The following configuration will give you total control over your Swagger definitions:
<?php
// api/src/Entity/Product.php
namespace App\Entity;
use ApiPlatform\Core\Annotation\ApiResource;
use ApiPlatform\Core\Annotation\ApiProperty;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
use Symfony\Component\Validator\Constraints as Assert;
/**
* @ApiResource
* @ORM\Entity
*/
class Product // The class name will be used to name exposed resources
{
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="integer")
* @ORM\Id
* @ORM\GeneratedValue(strategy="AUTO")
*/
public $id;
/**
* @param string $name A name property - this description will be avaliable in the API documentation too.
*
* @ORM\Column
* @Assert\NotBlank
*
* @ApiProperty(
* attributes={
* "swagger_context"={
* "type"="string",
* "enum"={"one", "two"},
* "example"="one"
* }
* }
* )
*/
public $name;
/**
* @ORM\Column
* @Assert\DateTime
*
* @ApiProperty(
* attributes={
* "swagger_context"={"type"="string", "format"="date-time"}
* }
* )
*/
public $timestamp;
}Or in YAML:
# api/config/api_platform/resources.yaml
resources:
App\Entity\Product:
properties:
name:
attributes:
swagger_context:
type: string
enum: ['one', 'two']
example: one
timestamp:
attributes:
swagger_context:
type: string
format: date-timeWill produce the following Swagger documentation:
{
"swagger": "2.0",
"basePath": "/",
"definitions": {
"Product": {
"type": "object",
"description": "This is a product.",
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "integer",
"readOnly": true
},
"name": {
"type": "string",
"description": "This is a name.",
"enum": ["one", "two"],
"example": "one"
},
"timestamp": {
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time"
}
}
}
}
}# Changing the Name of a Definition
API Platform generates a definition name based on the serializer groups defined
in the (de)normalization_context. It’s possible to override the name
thanks to the swagger_definition_name option:
/**
* @ApiResource(
* collectionOperations={
* "post"={
* "denormalization_context"={
* "groups"={"user_read"},
* "swagger_definition_name": "Read",
* },
* },
* },
* )
*/
class User
{
}It’s also possible to re-use the (de)normalization_context:
/**
* @ApiResource(
* collectionOperations={
* "post"={
* "denormalization_context"=User::API_WRITE,
* },
* },
* )
*/
class User
{
const API_WRITE = [
'groups' => ['user_read'],
'swagger_definition_name' => 'Read',
];
}# Changing Operations in the Swagger Documentation
You also have full control over both built-in and custom operations documentation:
resources:
App\Entity\Rabbit:
collectionOperations:
create_user:
method: get
path: '/rabbit/rand'
controller: App\Controller\RandomRabbit
swagger_context:
summary: Random rabbit picture
description: >
# Pop a great rabbit picture by color!

requestBody: '{"days": 23}'
parameters:
- {name: 'theme', description: 'dark'}
# Changing the Swagger UI Location
Sometimes you may want to have the API at one location, and the Swagger UI at a different location. This can be done by disabling the Swagger UI from the API Platform configuration file and manually adding the Swagger UI controller.
# Disabling Swagger UI
# api/config/packages/api_platform.yaml
api_platform:
# ...
enable_swagger_ui: false# Manually Registering the Swagger UI Controller
# app/config/routes.yaml
swagger_ui:
path: /docs
controller: api_platform.swagger.action.uiChange /docs to your desired URI you wish Swagger to be accessible on.
# Using the Swagger Command
You can also dump your current Swagger documentation using the provided command:
$ docker-compose exec php bin/console api:swagger:export
# Swagger documentation in JSON format...# Overriding the UI Template
As described in the Symfony documentation, it’s possible to override the Twig template that loads Swagger UI and renders the documentation:
{# templates/bundles/ApiPlatformBundle/SwaggerUi/index.html.twig #}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>{% if title %}{{ title }} {% endif %}My custom template</title>
{# ... #}
</html>You may want to copy the one shipped with API Platform and customize it.
# Enable Swagger doc for API Gateway
AWS API Gateway supports Swagger 2.0 partially, but it requires some changes. Fortunately, API Platform provides a way to be compatible with both Swagger 2.0 & API Gateway.
To enable API Gateway compatibility on your Swagger doc, add api_gateway=true query parameter:
http://www.example.com/docs.json?api_gateway=true
You can also help us improve the documentation of this page.
